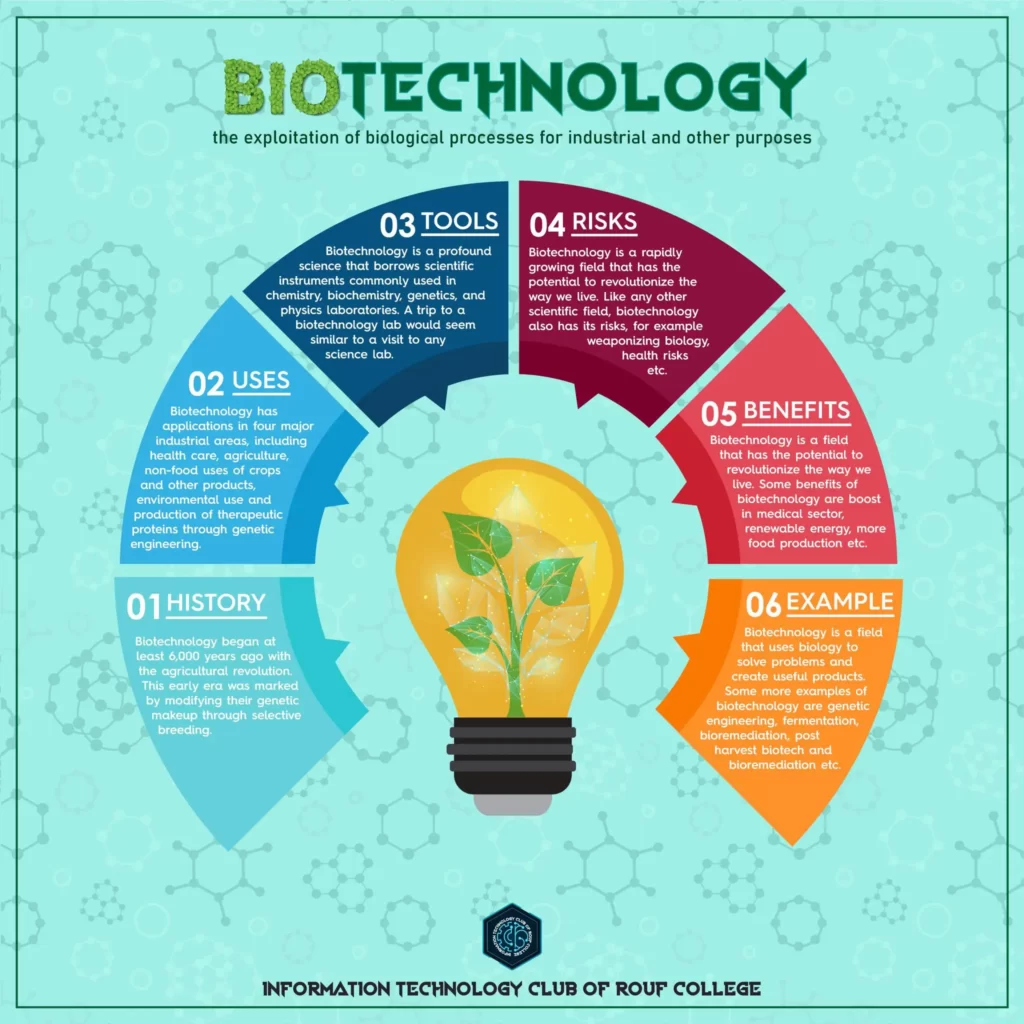
Biotechnology
Article Credit: Arko Famin
In the realm of modern science, biotechnology stands as a testament to human ingenuity and curiosity. This groundbreaking field merges biology, technology, and engineering to manipulate living organisms at the molecular and cellular level. With its profound impact on various sectors including medicine, agriculture, and environmental conservation, biotechnology has redefined the boundaries of capabilities.
At its core, biotechnology harnesses the power of living organisms to create products and processes that enhance human lives. The foundation of biotechnology lies in understanding the intricate machinery of cells, DNA, and proteins. Scientists employ cutting-edge techniques such as genetic engineering, molecular cloning, and genome editing to modify and manipulate genetic material. This intricate manipulation allows for the creation of novel traits, improved characteristics, and the development of entirely new organisms.
Key Concepts and Techniques:
Genetic Engineering: Central to biotechnology is the ability to alter an organism’s genetic build.
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): PCR is a technique used to amplify DNA segments, making it an essential tool for DNA analysis, forensics, and disease diagnosis.
Cryosurgery: Cryosurgery is a medical technique that uses extremely cold temperatures to freeze and destroy abnormal or diseased tissue. It’s often used to treat skin lesions, certain types of cancer, and various medical conditions.
The CRISPR-Cas9 system has transformed genome editing, allowing scientists to precisely modify genes with unprecedented accuracy.
Biotechnology has led to groundbreaking medical advancements, including personalized medicine, gene therapies, and biopharmaceuticals. It has the potential to cure previously incurable diseases by correcting faulty genes and engineering tissues.Crop improvement cultivates agriculture through enhanced yields, nutritional content, and resistance to pests and diseases.Bioremediation uses microorganisms to clean up polluted environments, while synthetic biology creates biofuels and sustainable materials, reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.
The future of biotechnology indicating advancements in synthetic biology, bioinformatics, and nanotechnology promise to open new avenues for solving global challenges, from curing rare genetic disorders to mitigating the effects of climate change.
